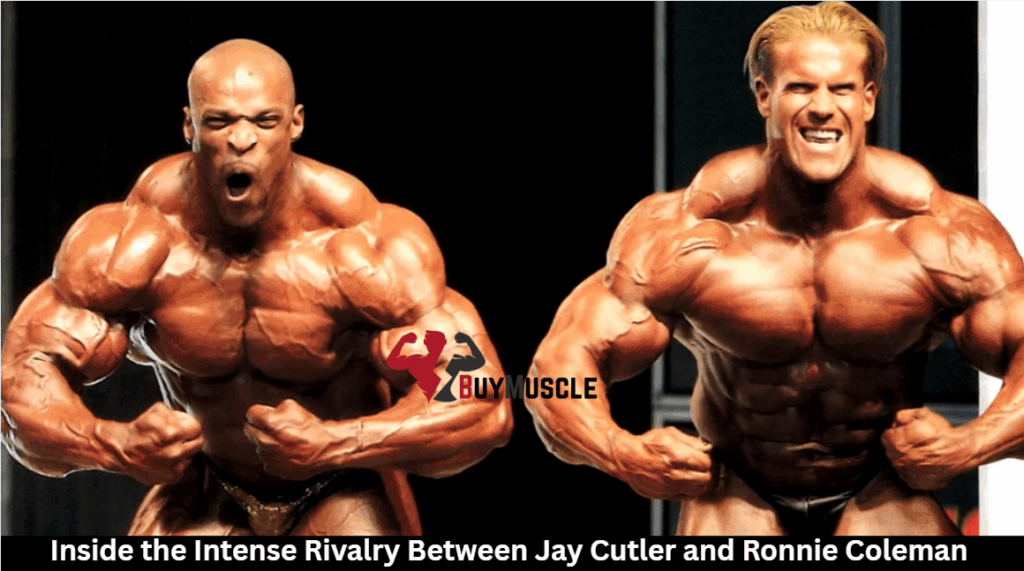
Inside the Intense Rivalry Between Jay Cutler and Ronnie Coleman
The fight between Jay Cutler and Ronnie Coleman is the most famous in bodybuilding history. Coleman won Mr. Olympia eight years in a row from 1998 to 2005 with his huge “mass monster” body. Cutler, on the other hand, chased him with precise aesthetics and strategic improvements. Cutler finally beat Coleman in 2006 after years […]
Inside the Intense Rivalry Between Jay Cutler and Ronnie Coleman Read More »