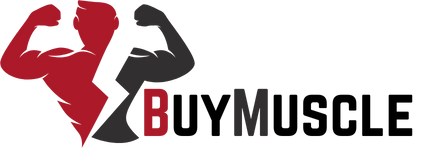The adrenal glands produce cortisol, which controls metabolism, inflammation, and the stress response. The body needs this hormone for short bursts of survival as it responds to immediate stress.
Yet elevated cortisol can impair muscle strength and growth. Cortisol levels increase muscle breakdown, decrease recovery, and blunt body anabolic processes necessary for strength building.
Understanding Cortisol’s Impact on Muscle Strength
Cortisol is classified as a catabolic hormone, meaning it promotes the breakdown of complex molecules, including muscle proteins, into simpler ones for immediate energy use. While this mechanism is essential during acute stress, prolonged activation leads to muscle wasting.
Prolonged high cortisol levels can inhibit protein synthesis, slow down recovery from workouts, and weaken performance over time. When cortisol imbalance is present, athletes and highly active individuals may experience symptoms such as persistent fatigue, declining strength, poor sleep quality, and an increased susceptibility to injury.
Recognizing these signs is essential for addressing the underlying stressors before they lead to significant strength loss from high cortisol exposure.
Key Causes of Elevated Cortisol
Several factors can cause cortisol levels to spike beyond healthy limits. Chronic psychological stress stemming from work, relationships, or financial worries is one of the primary drivers.
Overtraining is another critical contributor. When the body does not have sufficient time to recover from intense exercise sessions, cortisol remains elevated to deal with the constant physical demand.
Lifestyle factors, including poor sleep habits, excessive caffeine intake, and nutritional deficiencies, increase cortisol production. When combined, they create a cycle that prevents the body from repairing and building muscle tissue.
Natural Ways to Lower Cortisol and Preserve Muscle

Managing cortisol levels is essential for maintaining muscle mass and strength. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, controlled breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices, can help regulate the body’s stress response.
Sleep optimization is equally important. Deep, restorative sleep supports hormone balance, enhances recovery, and naturally lowers cortisol. Creating a dark, cool, and quiet sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality.
Prioritizing recovery through planned deload weeks, massages, and active rest days allows muscles to rebuild without the constant catabolic threat of elevated cortisol levels. Active rest days involving light and enjoyable movement are particularly helpful in maintaining momentum while promoting recovery.
Nutrition for Cortisol Control
Food choices have a profound impact on cortisol regulation. Anti-inflammatory foods such as dark leafy greens, fatty fish like salmon, and antioxidant-rich berries help combat the oxidative stress that can trigger excess cortisol production.
Stable blood sugar levels are also crucial. Frequent blood sugar spikes and crashes can stimulate cortisol release, so aim for balanced meals that contain protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
Several supplements support adrenal health and help naturally regulate cortisol levels. Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha lower cortisol. Magnesium supports muscle relaxation and stress regulation, while vitamin C plays a direct role in moderating the body’s response to stress.
Training Strategies to Combat Cortisol
Exercise is a powerful tool for both raising and lowering cortisol, depending on how you manage it. Smart programming during stressful periods focuses on balancing training intensity with sufficient recovery.
Strength-focused, lower-volume workouts are more beneficial during times of high stress. They allow individuals to maintain and even build strength without placing excessive systemic stress on the body.
Minimize excessive cardio or high-repetition schemes if you already have elevated cortisol levels. These training styles can exacerbate muscle breakdown and slow recovery, undermining efforts to preserve strength.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Hormonal Health
Simple lifestyle adjustments can dramatically affect cortisol levels. Reducing stimulant intake, particularly caffeine, during recovery phases helps prevent unnecessary adrenal stimulation.
Scheduling downtime that includes non-fitness hobbies, such as reading, painting, or spending time in nature, provides essential psychological relief, allowing the body to shift out of a constant fight-or-flight mode.
Finally, building a sustainable daily routine that balances work, training, rest, and leisure activities lays the foundation for long-term hormonal health and strength maintenance. Consistency, rather than intensity, becomes the guiding principle in fighting cortisol and keeping muscle during stressful times.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does stress cause muscle loss?
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which promotes muscle protein breakdown and impairs the body’s ability to repair and grow muscle tissue.
What foods help lower cortisol?
Antioxidant-rich foods and healthy fats, such as dark leafy greens, berries, fatty fish, avocados, and nuts, naturally help combat cortisol and promote hormonal balance.
Should I reduce exercise intensity when stressed?
During periods of high stress, it’s advisable to reduce exercise intensity and focus on strength-based, lower-volume workouts to prevent overtraining and muscle damage.